c++11标准给广大c++程序员提供了非常强大的武器库。今天我们就利用c++11中的std::thread 实现一个半同步半异步的线程池。
首先简单介绍一下线程池。
线程池是为了解决大量的短时任务频繁的创建销毁线程造成性能开销的一个技术。在程序开始时创建一定量的线程。当有任务到达时,从池中选出空闲线程来处理任务,当任务处理完成再将线程返回到池中。
线程池实现有两种模型:1.半同步半异步模型。2.领导者跟随者模型。
半同步半异步模型原理图:
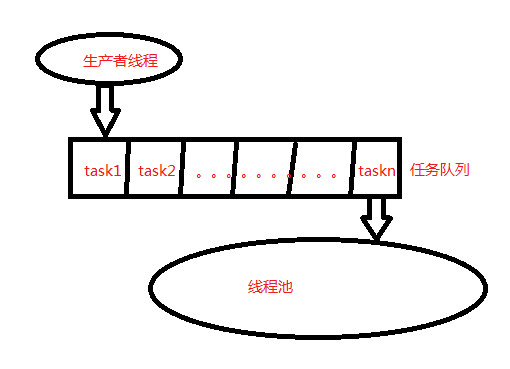
原理
同步层:通过线程将处理任务添加到队列中,这个过程是同步执行的。
队列层:所有的任务都会放到这里,上层放任务到这里,下层从这里取任务。
异步层:事先创建好线程,让线程不断的去处理队列层的任务。上层不关心这些,只负责把任务放入队列,所有对上层来说这里是异步的。
代码实现:
任务队列:TaskQueue.h
#pragma once
#include <list>
#include <mutex>
#include <thread>
#include <condition_variable>
#include <iostream>
//队列层
template<typename T>
class TaskQueue
{
public:
TaskQueue(int maxsize) : m_maxSize(maxsize), m_needStop(false) {}
~TaskQueue() {}
//添加事件,左值拷贝,右值移动
void Put(const T& x)
{
Add(x);
}
void Put(T && x)
{
Add(x);
}
//从队列中取事件,取所有事件
void Take(std::list<T> &list)
{
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> locker(m_mutex);
//满足条件则唤醒 不满足就阻塞
m_notEmpty.wait(locker, [this](){
return m_needStop || NotEmpty();
});
if (m_needStop)
{
return;
}
list = std::move(m_queue);
//唤醒其他阻塞的线程
m_notFull.notify_one();
}
void Take(T &t)
{
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> locker(m_mutex);
m_notEmpty.wait(locker, [this](){
return m_needStop || NotEmpty();
});
if (m_needStop)
{
return;
}
t = m_queue.front();
m_queue.pop_front();
m_notFull.notify_one();
t();
}
//停止所有线程在队列中读取
void Stop()
{
{
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> locker(m_mutex);
m_needStop = true;
}
m_notFull.notify_all();
m_notEmpty.notify_all();
}
//队列为空
bool Empty()
{
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> locker(m_mutex);
return m_queue.empty();
}
//队列为满
bool Full()
{
std::try_guard<std::mutex> locker(m_mutex);
return m_queue.size() == m_maxSize;
}
//队列大小
size_t Size()
{
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> locker(m_mutex);
return m_queue.size();
}
private:
//往队列里添加事件,事件是泛型的,通过std::function封装为对象
template<typename F>
void Add(F &&x)
{
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> locker(m_mutex);
m_notFull.wait(locker, [this](){
return m_needStop || NotFull();
});
if (m_needStop)
{
return;
}
m_queue.push_back(std::forward<F>(x));
m_notEmpty.notify_one();
}
//队列未满
bool NotFull() const
{
bool full = m_queue.size() >= m_maxSize;
if (full)
{
std::cout << "queue is full" << std::endl;
}
return !full;
}
//队列未空
bool NotEmpty() const
{
bool empty = m_queue.empty();
if (empty)
{
std::cout << "queue is empty...wait" << std::endl;
std::cout << "thread id:" << std::this_thread::get_id() << std::endl;
}
return !empty;
}
private:
std::mutex m_mutex; // 互斥锁
std::list<T> m_queue; //任务队列
std::condition_variable m_notEmpty; //队列不为空条件变量
std::condition_variable m_notFull; //队列不为满条件变量
int m_maxSize; //任务最大长度
bool m_needStop; //终止标识
};线程池:ThreadPool.h
#pragma once
#include <functional>
#include <thread>
#include <memory>
#include <atomic>
#include "TaskQueue.h"
const int MAX_TASK_COUNT = 100;
class ThreadPool
{
public:
//规定任务类型为void(),我们可以通过c++11不定参数模板来实现一个可接受任何参数的范式函数模板,
//这样就是一个可以接收任何任务的任务队列了
using Task = std::function<void()>;
//hardware_concurrency 检测硬件性能,给出默认线程数
ThreadPool(int numThreads = std::thread::hardware_concurrency());
//销毁线程池
~ThreadPool();
//终止所有线程,call_once保证函数只执行一次
void Stop();
//添加任务,普通版本
void AddTask(const Task &task);
//添加任务,右值引用版本
void AddTask(Task && task);
private:
//停止线程池
void StopThreadGroup();
void Start(int numThreads);
//一次取出所有事件
void RunInThreadList();
//一次取出一个事件
void RunInThread();
private:
//线程池
std::list<std::shared_ptr<std::thread>> m_threadGroup;
//任务队列
TaskQueue<Task> m_queue;
//原子布尔值
std::atomic_bool m_running;
//辅助变量->call_once
std::once_flag m_flag;
};ThreadPool.cpp
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "ThreadPool.h"
ThreadPool::ThreadPool(int numThreads/* = std::thread::hardware_concurrency()*/)
: m_queue(MAX_TASK_COUNT)
{
Start(numThreads);
}
//销毁线程池
ThreadPool::~ThreadPool()
{
Stop();
}
//终止所有线程,call_once保证函数只执行一次
void ThreadPool::Stop()
{
std::call_once(m_flag, [this](){ StopThreadGroup(); });
}
//添加任务,普通版本
void ThreadPool::AddTask(const Task &task)
{
m_queue.Put(task);
}
//添加任务,右值引用版本
void ThreadPool::AddTask(Task && task)
{
m_queue.Put(std::forward<Task>(task));
}
//停止线程池
void ThreadPool::StopThreadGroup()
{
m_queue.Stop();
m_running = false;
for (auto thread : m_threadGroup)
{
if (thread)
{
thread->join();
}
}
m_threadGroup.clear();
}
void ThreadPool::Start(int numThreads)
{
m_running = true;
for (int i = 0; i < numThreads; ++i)
{
//智能指针管理,并给出构建线程的参数,线程调用函数和参数
std::cout << "create thread pool " << i << std::endl;
m_threadGroup.push_back(std::make_shared<std::thread>(&ThreadPool::RunInThread, this));
}
}
//一次取出所有事件
void ThreadPool::RunInThreadList()
{
while (m_running)
{
std::list<Task> list;
std::cout << "take" << std::endl;
m_queue.Take(list);
for (auto &task : list)
{
if (!m_running)
{
return;
}
task();
}
}
}
//一次取出一个事件
void ThreadPool::RunInThread()
{
std::cout << m_queue.Size() << std::endl;
while (m_running)
{
Task task;
if (!m_running)
{
return;
}
m_queue.Take(task);
}
}main.cpp
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "ThreadPool.h"
#include <chrono>
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
ThreadPool pool;
//创建线程向任务队列添加任务
std::thread thd1([&pool](){
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
auto thid = std::this_thread::get_id();
pool.AddTask([thid, i](){
std::cout << "ThreadID:" << thid << " Task " << i << " Done!" << std::endl;
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(500));
});
}
});
thd1.join();
pool.Stop();
system("pause");
return 0;
}结果:
TheadID:5779 Task 1 Done!
TheadID:5779 Task 2 Done!
TheadID:5779 Task 3 Done!
TheadID:5780 Task 4 Done!
TheadID:5779 Task 5 Done!
TheadID:5779 Task 6 Done!
TheadID:5779 Task 7 Done!
TheadID:5779 Task 8 Done!
TheadID:5779 Task 9 Done!