操作系统:ubuntu10.10
前言:
在稍微大点的项目中,基本都会遇到算法问题,特别是大数据的查找。
在当前项目中,使用到了哈希链表。
一,概述
实现思路:用数组保存哈希桶的关键信息,再用链表链接数据到对应的哈希桶中。
如:管理很多字符串。以a~z,?为哈希桶。
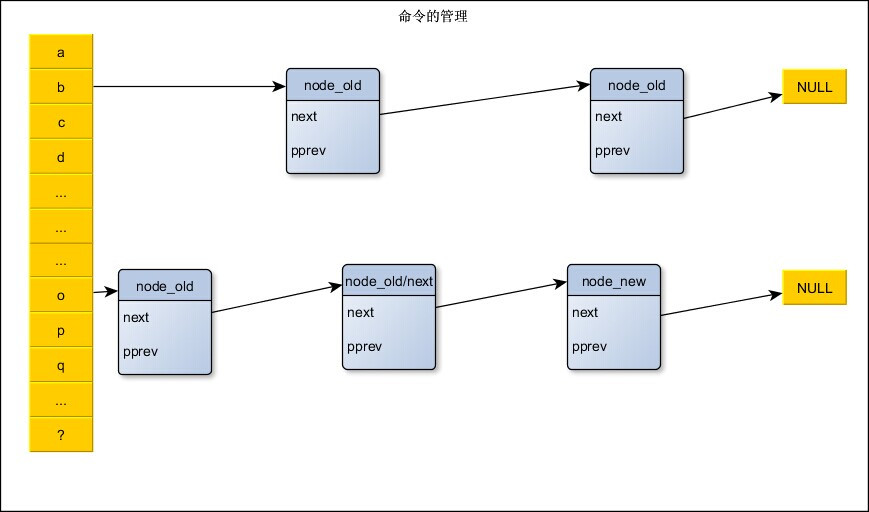
二,实现
1,结构
struct hlist_node
{
struct hlist_node *next; // 指向下一个结点的指针
struct hlist_node **pprev;// 指向上一个结点的next指针的地址
};
struct hlist_head
{
struct hlist_node *first; // 指向每一个hash桶的第一个结点的指针
};2,初始化哈希桶
// 初始化hash桶的头结点 #define INIT_HLIST_HEAD(ptr) ((ptr)->first = NULL)

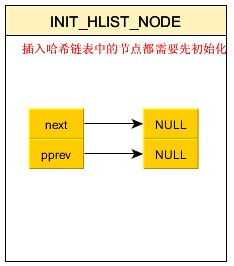
3,初始化哈希桶中的每一个节点
// 初始化hash桶的普通结点
static inline void INIT_HLIST_NODE(struct hlist_node *node)
{
node->next = NULL;
node->pprev = NULL;
}
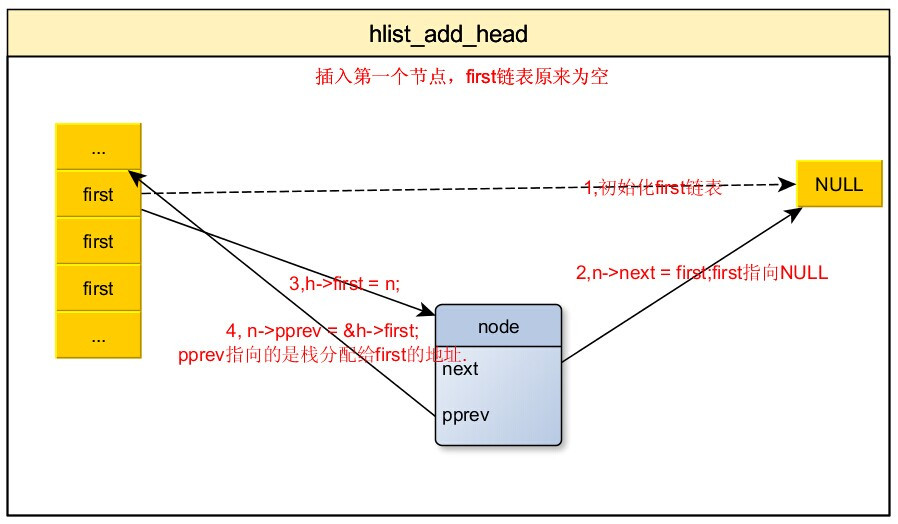
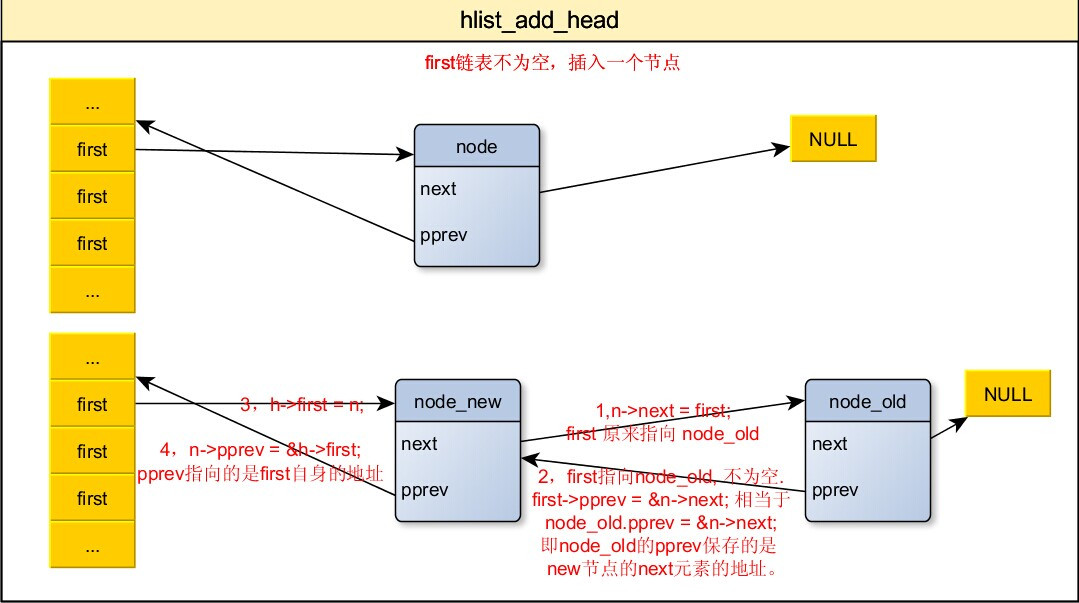
4,添加节点到哈希桶中
/**
* hlist_add_head
* @n: the element to add to the hash list.
* @h: the list to add to.
*/
static inline void hlist_add_head(struct hlist_node *n,struct hlist_head *h)
{
struct hlist_node *first = h->first;
n->next = first;
if (first)
first->pprev = &n->next;
h->first = n;
n->pprev = &h->first;
}
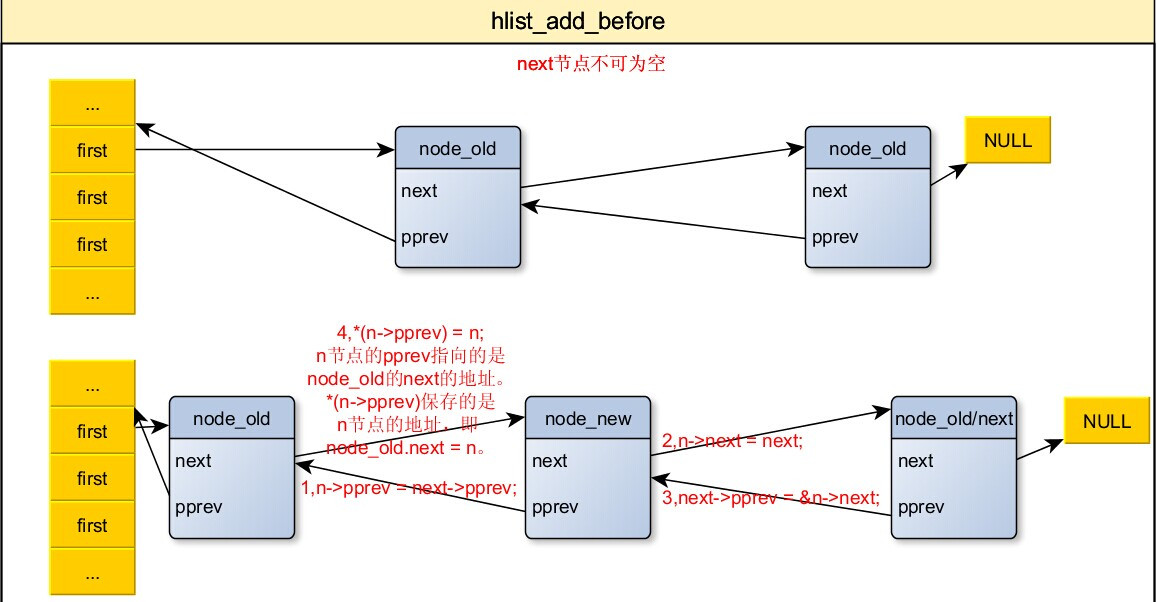
5,把节点插入到指定节点前面
/* next must be != NULL */
/* n:要添加的新的节点。
* next:在next节点之前添加n。
* 在next节点的前面添加一个新的节点n,在使用这个函数中要特别注意,next不能为NULL。
*/
static inline void hlist_add_before(struct hlist_node *n,
struct hlist_node *next)
{
n->pprev = next->pprev;
n->next = next;
next->pprev = &n->next;
*(n->pprev) = n;
}
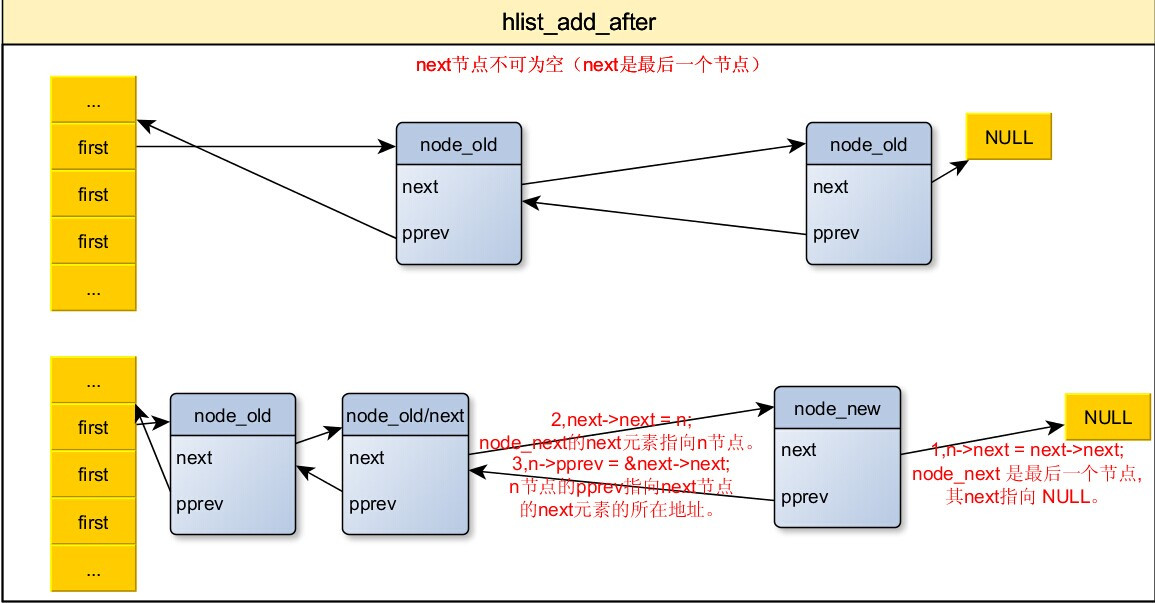
6,把节点插入到指定节点之后
/* next must be != NULL */
/* n:要添加的新的节点。
* next:表示在next节点之后添加n。
* 在next 节点的后面添加一个新的节点n,这里也要求next不能为NULL
*/
static inline void hlist_add_after(struct hlist_node *n,
struct hlist_node *next)
{
n->next = next->next;
next->next = n;
n->pprev = &next->next;
if(n->next)
n->next->pprev = &n->next;
}
7,删除节点
/* n:要删除的节点。
* 对于删除操作的话,要注意n是不是末尾节点,如果是末尾节点的话,next就是NULL?
* 所以就没有指向的pprev,就更不能进行相应的修改了,否则进行修改。
*/
static inline void __hlist_del(struct hlist_node *n)
{
struct hlist_node *next = n->next;
struct hlist_node **pprev = n->pprev;
*pprev = next;
if (next)
next->pprev = pprev;
}
/* n:要删除的节点。
* 在这个函数中首先删除了n节点,之后将n节点的两个指针指向了LIST_POSION,表示不可使用的地方
*/
static inline void hlist_del(struct hlist_node *n)
{
__hlist_del(n);
n->next = LIST_POISON1;
n->pprev = LIST_POISON2;
}8,判断节点是否在哈希桶中
/*
* 判断一个结点是否已经存在于hash桶中
* 判断h->prev是不是为空,如果pprev的指向是空的话,表示这个节点没有添加到这个链表当中来,
* 如果是空,返回true,否则返回false
*/
static inline int hlist_unhashed(const struct hlist_node *h)
{
return !h->pprev;
}9,判断哈希桶是否为空
// 判断一个hash桶是否为空
/* h:struct hlist_head节点指针(hlist链表的头节点)。
* 判断hlist链表是不是空链表,如果是,返回true,否则返回false。
*/
static inline int hlist_empty(const struct hlist_head *h)
{
return !h->first;
}10,遍历
/* ptr:表示struct hlist_node类型的一个地址。
* type:结构体名
* member:type结构体中的hlist_node成员变量的名称
* 表示得到ptr所指地址的这个结构体的首地址
*/
#define hlist_entry(ptr, type, member) container_of(ptr,type,member)
/* pos:struct hlist_node类型的一个指针;
* head:struct hlist_head类型的一个指针,表示hlist链表的头结点。
* 这个实际上就是一个for循环,从头到尾遍历链表。
*/
#define hlist_for_each(pos, head) \
for (pos = (head)->first; pos != NULL ; 1; }); \
pos = pos->next)
/* 这个实际上就是一个for循环,从头到尾遍历链表。这个和前面的不同的是多了一个n,
* 这么做是为了遍历过程中防止断链的发生。删除时用这个。
* pos:struct hlist_node类型的一个指针;
* n:struct hlist_node类型的一个指针;
* head:struct hlist_head类型的一个指针,表示hlist链表的头结点。
*/
#define hlist_for_each_safe(pos, n, head) \
for (pos = (head)->first; pos && ({ n = pos->next; 1; }); \
pos = n)
/* tops:用来存放遍历到的数据结构的地址,类型是type *;
* pos:struct hlist_node类型的一个指针;
* head:hlist链表的头结点;
* member:struct hlist_node在type结构体中的变量的名称。
* 在循环中,我们就可以使用tops来指向type类型结构体的任何一个变量了。
*/
/**
* hlist_for_each_entry - iterate over list of given type
* @tpos: the type * to use as a loop cursor.
* @pos: the &struct hlist_node to use as a loop cursor.
* @head: the head for your list.
* @member: the name of the hlist_node within the struct.
*/
#define hlist_for_each_entry(tpos, pos, head, member) \
for (pos = (head)->first; \
(pos != NULL) && \
({ tpos = hlist_entry(pos, typeof(*tpos), member); 1;}); \
pos = pos->next)
/* tops:用来存放遍历到的数据结构的地址,类型是type *;
* pos:struct hlist_node类型的一个指针;
* n:struct hlist_node类型的一个指针;
* head:hlist链表的头结点;
* member:struct hlist_node在type结构体中的变量的名称。
* 在循环中,我们就可以使用tops来指向type
* 类型结构体的任何一个变量了。这个宏函数也是为了防止在遍历的时候删除节点而引入的。
*/
/**
* hlist_for_each_entry_safe - iterate over list of given type safe against
removal of list entry
* @tpos: the type * to use as a loop cursor.
* @pos: the &struct hlist_node to use as a loop cursor.
* @n: another &struct hlist_node to use as temporary storage
* @head: the head for your list.
* @member: the name of the hlist_node within the struct.
*/
#define hlist_for_each_entry_safe(tpos, pos, n, head, memsber) \
for (pos = (head)->first; \
pos && ({ n = pos->next; 1; }) && \
({ tpos = hlist_entry(pos, typeof(*tpos), member); 1;}); \
pos = n三,实例
/*
* hlist begin
*/
#define CMD_HASH_HEAD_SIZE 27
typedef struct _cmd_hash_head
{
struct hlist_head head; // 哈希桶的首地址
int8_t ch; // 哈希桶的关键字(a~z,?,总共27个)
int8_t offset; // 这个哈希桶在整个哈希表中的偏移
int16_t count; // 当前哈希桶中节点的个数
}cmd_hash_head_t;
typedef struct _cmd_hash_node
{
struct hlist_node node;
int8_t name[20];
}cmd_hash_node_t;
static cmd_hash_head_t cmd_hash[CMD_HASH_HEAD_SIZE];
static void cmd_hash_init(void)
{
int32_t index = 0;
memset(cmd_hash,0,sizeof(cmd_hash));
for(index = 0; index < (CMD_HASH_HEAD_SIZE - 1); index++)
{
INIT_HLIST_HEAD(&cmd_hash[index].head);
cmd_hash[index].count = 0;
cmd_hash[index].offset = index;
cmd_hash[index].ch = 'a' + index;
}
index = CMD_HASH_HEAD_SIZE - 1;
INIT_HLIST_HEAD(&cmd_hash[index].head);
cmd_hash[index].count = 0;
cmd_hash[index].offset = index;
cmd_hash[index].ch = '?';
}
static void cmd_hash_show(void)
{
int32_t index = 0;
for (index = 0; index < (CMD_HASH_HEAD_SIZE - 1); index++)
printf("hash%d,head : %p,count : %d,offset : %d,ch : %c\n",index,
cmd_hash[index].head,cmd_hash[index].count,cmd_hash[index].offset,cmd_hash[index].ch);
index = CMD_HASH_HEAD_SIZE - 1;
printf("hash%d,head : %p,count : %d,offset : %d,ch : %c\n",index,
cmd_hash[index].head,cmd_hash[index].count,cmd_hash[index].offset,cmd_hash[index].ch);
}
static void to_lower(int8_t *str)
{
int32_t len = 0;
int32_t index = 0;
if (str == NULL) return;
len = strlen((char*)str);
for (index = 0; index < len; index++)
{
str[index] = tolower(str[index]);
}
}
static int8_t node_type(int8_t *name)
{
int8_t ch = 0x00;
int8_t offset = 0;
if (name == NULL) return -1;
ch = name[0];
switch(ch)
{
case 'a':
case 'b':
case 'c':
case 'd':
case 'e':
case 'f':
case 'g':
case 'h':
case 'i':
case 'j':
case 'k':
case 'l':
case 'm':
case 'n':
case 'o':
case 'p':
case 'q':
case 'r':
case 's':
case 't':
case 'u':
case 'v':
case 'w':
case 'x':
case 'y':
case 'z':
offset = ch - 'a' + 0;
break;
default :
offset = 26;
break;
}
return offset;
}
//static cmd_hash_node_t ptr_buffer[100];
static void hash_node_init(int8_t *name)
{
int8_t offset = 0;
cmd_hash_node_t *node_ptr = (cmd_hash_node_t*)calloc(1,sizeof(cmd_hash_node_t));
offset = node_type(name);
if(offset < 0) return;
strlcpy(node_ptr->name, name, strlen((char*)name));
INIT_HLIST_NODE(&node_ptr->node);
hlist_add_head(&node_ptr->node,&cmd_hash[offset].head);
cmd_hash[offset].count++;
}
static void cmd_hash_node_init(void)
{
hash_node_init((int8_t*)"hello");
hash_node_init((int8_t*)"help");
hash_node_init((int8_t*)"scan");
hash_node_init((int8_t*)"???");
}
static void cmd_hash_node_show(void)
{
int32_t index = 0;
int16_t count = 0;
cmd_hash_node_t *entry = NULL;
struct hlist_node *ptr = NULL;
printf("display\n");
for (index = 0; index < CMD_HASH_HEAD_SIZE; index++)
{
count = cmd_hash[index].count;
if (count > 0)
{
printf("hash%d,head : %p,count : %d,offset : %d,ch : %c\n",index,
cmd_hash[index].head,cmd_hash[index].count,cmd_hash[index].offset,cmd_hash[index].ch);
hlist_for_each_entry(entry,ptr, &cmd_hash[index].head, node)
{
printf(" name : %s\n",entry->name);
}
}
}
}
static void test_hlist_oper(void)
{
cmd_hash_init();
cmd_hash_show();
cmd_hash_node_init();
cmd_hash_show();
cmd_hash_node_show();
}
static void test_hlist(void)
{
test_hlist_oper();
}
/*
* hlist end
*/结果:
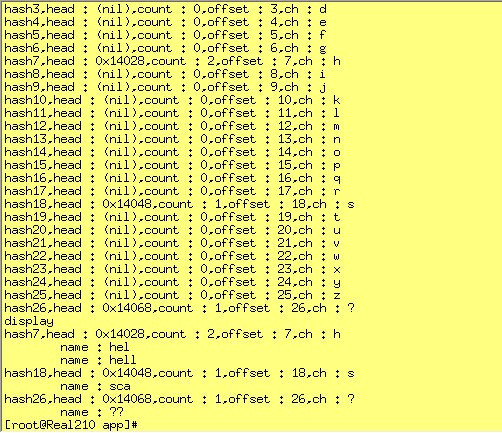
四,参考
linux内核源码
收藏的用户(0)
X
正在加载信息~
2
最新回复 (0)

